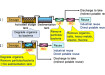
Flash Point of fuels to assess their flammability and safety characteristics
Flash Point testing is a critical evaluation method used in the field of fuels to assess their flammability and safety characteristics. It is a crucial parameter in understanding how easily a fuel can ignite and subsequently pose risks during storage, transportation, and handling.
During Flash Point testing, a small sample of the fuel is heated in a controlled environment. The temperature at which it releases enough vapor to form a flammable mixture with the air and produce a momentary flash of fire when exposed to an open flame or spark is the Flash Point. This temperature is a fundamental indicator of a fuel's volatility, indicating the lowest temperature at which it can catch fire under specific conditions.
The Flash Point test helps categorize fuels into different classes, such as flammable or combustible, and is vital for safety regulations and guidelines. Fuels with a higher Flash Point are considered less prone to ignition, making them safer for storage and transport.
Understanding the Flash Point of a fuel is crucial for ensuring safe handling and storage practices, especially in industries like petrochemicals, where flammable liquids are commonplace. By assessing the Flash Point, companies and regulatory bodies can implement appropriate safety measures to prevent accidents, fires, and explosions associated with the use and transportation of these fuels.
Events
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
May 13 2024 Munich, Germany
May 23 2024 Beijing, China
May 23 2024 Beijing, China
Jun 10 2024 Algiers, Algeria